Agent极简入门
【核心概念】
Agent:可以自主完成任务目标的智能体。最基本的两个特点:自主性(Autonomous)、目标导向(Goal-Oriented)。Agent是概念,具体的实现内涵是灵活的,目前的主流模式是:LLM/VLM 提供决策能力,Function Calling API提供执行能力/工具(tools)。
System Prompt:设定Agent角色和引导Agent行为的文本。
Context:Agent做决策时,所参考的环境信息,包括对话历史、知识库、工具集,等等。
【参考资料】
时代主题:两国博弈
两国在进行全领域博弈。更核心的主题是:高科技领域争霸。因为,“科学技术是第一生产力”。
子领域:
- 能源。谁能利用的能源量级大,谁的能源生产便宜,谁胜出。石油、天然气、电力、太阳能、风能、核聚变。
- 工业生产制造能力。全工业门类,高精特新技术。例如
- 汽车生产制造,
- 船泊生产制造,
- 以AI体系为主的软硬件能力,例如,AI模型、操作系统、芯片、存储、机器人等,
- 航空航天生产制造,
- 新材料生产制造。
- 矿业。
- 先进医学/医疗体系
- 人口/人才吸引,教育体系
- 金融/货币
- 粮食生产/种子/基因技术
- 外贸关系
在AI方面,黄仁勋提出的5层竞争模型:
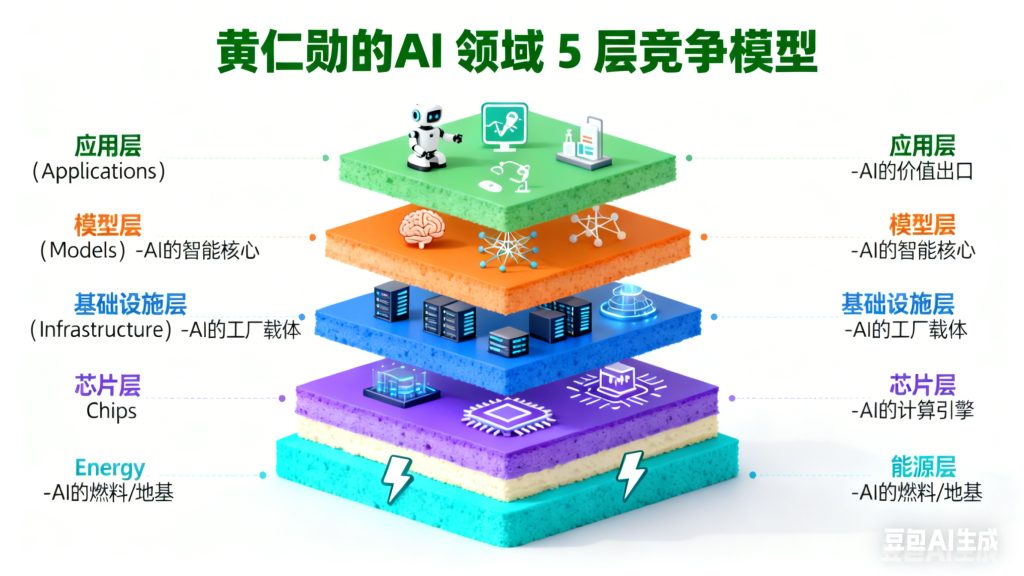
对我们的启示:
国内政策会大力扶植每一层中的龙头企业,以加强AI全局的竞争能力。这个过程会有泡沫,但是正向的泡沫。
国内也会期望出现类似于马斯克、黄仁勋、Altman等人的新一批高新技术产业的企业家人群,来替换掉早一代的企业家人群。
从LLM到Agent
技术热点从LLM转到了Agent,在发生着什么。
- 对于AI的衡量标准,从对话形式的榜单测试,转到了完成现实中具体任务的能力。
- 除了应用scaling law继续推高单个模型的能力上限以外,单模型迭代求解和多模型分工协作的能力提升方式,发挥空间更大。
- AI的自主行为能力(自主思考、自主决策、自主发现、反思)等能力,比执行固定工作流的能力更重要。
- AI context从对话历史上下文,开始拓展到全环境上下文(多模态、多输入源、多背景知识)。
综上,AI正在从实验和研究领域走向生活和生产领域,解决各种应用问题,创造真正的经济价值。
这给我们的提示:
未来并不会有太多做基模的人和有条件做基模的人。计算资源和数据规模,已经构成了准入门槛。做基模研发的投入产出比在变得越来越低。更多的人需要做:1)基模以后的AI能力提升方式研究。2)AI能力封装成AI应用,解决现实问题。
学物理的同学,系统思维比较好
宋飏
姚顺宇
Geoffrey Hinton
李飞飞
马斯克
统计物理的学习会培养人的系统思维。
个体需要全面拥抱AI
- 把自己手上要完成的工作,尝试尽量用AI工具来快速完成。借助AI工具,能5分钟完成的事情,不要花5个小时。包括,但不限于:
- 不要相信自己手写的代码,好过AI生成的。
- 不要认为自己苦思冥想憋出来的,或者老师给的论文想法,就是好想法。多和各种AI来交流,看他们如何评价你要做的idea,听听他们有没有更好的想法。
- 不要从头到尾读一个长文档/代码库/论文,交给AI做总结、摘要重点、画脑图,快速把握主旨。
- 遇到不懂的知识点,不要去检索了,直接问AI,并且可以要求AI进一步解释、拓展到相关的知识点、给出具体的例子等。
- 不要认为自己一句句手写的论文/邮件/汇报文档/PPT,就质量很高。把想写的内容,大概描述给AI,让AI帮写,然后自己进行校对。
- 让AI介入到自己的生活管理中。
- 自己的信息记录、日程管理、健康管理、相册、财务规划等,都交给可信任的AI。借助于AI,更好的了解自己的状态,把握自己的优势和不足。
- 借助于AI来辅助自己做一些生活决策。
- 未来Agent能力继续提升后,把需要处理的生活琐事交给agent来执行。例如,点外卖、充话费等。
- 对自己的社会角色,不设限。用AI实现自己大脑里萌发出的各种创意性想法。
- 做网站,APP,发短视频,做音乐,PS照片,写小说,画漫画,等等。
《天地孤影任我行》
对生活状态要做理性客观的评估
很多人焦虑的原因,并不是自己的生活状态绝对不好,而是不如别人好。应当对自己生活状态做理性客观的评估。
- 无刚性问题,便已经超过了很多的人。
- 刚性问题,包括:身体健康问题(痛苦的慢性病、绝症等),纠纷问题(法律纠纷、财务纠纷、人际纠纷、情感纠纷)。
- 病人只有一个愿望,健康的人有无数个愿望。
- 有覆盖生活成本的收入,并能产生结余,也已经超过了很多的人。
- 吃不饱时只有一个烦恼,吃饱了有无数个烦恼。
- 其他加分项:
- 友好的家人。
- 有同频的朋友可沟通。
- 有精神补充源:读书、运动、音乐等。
- 有被需要、可以提携别人的渠道。
- 有未来的希望。
- 过于被焦虑的项:
- 房贷:还的上就还,还不上就清理资产,换个负担的起的。
- 裁员:无非换个地方工作而已,只要自己是被社会需要的劳动力,是有工作机会的。可能还会是人生的一次转机。根本解法是,保证自己是个身体健康、有思想、有能力、有价值的人。
- 别人的负面评价:如果说的对,确实要听、要改;如果说的不对,或只是被情绪发泄,当他是个智力未开或是情绪不稳定的可怜虫,包容他吧。
- 容易被低估的项:
- 睡眠质量。长期来看,很重要,几乎决定个人日常状态和寿命。
- 食物结构。食药同源,吃的东西会影响身体状态。应该尽量做到健康的饮食习惯。
- 精神空虚/压抑。脑袋空空,刷短视频,注意力不能集中,无法进入深度思考状态,长期会积累精神方面的问题。
尽量进入正循环
正循环的范式:
行动->得到正面激励—>行动的动力增强—>更积极的行动—>得到更多的正面激励—>…..
负循环的范式:
行动->得到负面激励/未得到激励—>行动的动力削弱—>更消极的行动—>更得不到激励—>…..
【具体的例子】
个体的知识和成长方面:
个体的知识落后—>出于自我保护的封闭—>知识输入面窄—>没有进步继续落后—>….
人际关系方面:
不熟—>沟通少—>误会和猜忌—>进一步疏远—>更不熟—>…..
理财方面:
交易失败—>交易心态崩溃—>交易动作变形—>交易进一步失败—>….
【策略】
上面的循环,是一阶马尔科夫链。当进入到一种负循环时,有两种破局之法:1)清零,重新出发。2)更改其中一环的结果。
理解AI技术的意义—定性篇
定性,是通过逻辑思考,构建一个概念框架,把具体的事情,进行抽象和定义后,置于概念框架中的合理位置上。
【新工具论】
AI技术的产生对于人类的宏观意义是:人类又多了一种帮助自己更好的认识世界和改造世界的工具。这种新工具相比于其他出现过的工具,因智慧能力的超越性,异常强大。
【AI工具的两种功用:智力加持 和 行动替代】
认识世界是一种脑力劳动,主要包括:认知、记忆、思考。AI在认识世界方面,会为我们提供智力加持的作用,可以为扮演“外挂大脑”的角色。这部分AI技术对应的是具有理解、记忆、推理能力的大模型技术。AI在拥有了世界知识以后,可以对接用户所有的信息流入源,帮用户理解、记忆和推理信息,辅助用户进行学习、工作和生活。
帮助人类认识世界,这是未来的一大类AI应用场景。目前的豆包、Gemini属于这一类AI功用范畴。这一类AI功能应用,更重要的是:1)触达到用户数据,越多、越私密,越好。2)具有强大的数据分析和深度思考能力。
改造世界是一种体力劳动,主要包括:理解环境、设定目标、规划策略,执行策略以创造结果。AI在改造世界方面,会为我们提供行动替代的作用。这部分AI技术对应的是具有环境感知和环境交互能力的Agent技术。AI Agent可以接收任务指令,执行策略,完成具体的操作过程,达到任务目标。
帮助人类改造世界,这是未来的另一大类AI应用场景。目前的Manus、手机端的执行助手属于这一类AI功用范畴。这一类功能应用,更重要的是:1)精准且垂直的定义场景。2)agent的自进化能力。3)物联网(IOT)生态的发展。
发现了長渕剛
長渕剛,歌手音乐风格,有点像伍佰。简单直接,情感真挚。《トンボ/蜻蛉》,《乾杯》。
世界模型
学习问题是估计$P_{\theta}(World)$。
推理/应用问题是使用$P_{\theta}(World)$进行生成/反馈/推演。
惊闻,遗憾
突闻一位之前熟悉的AI创业者骤然离世。和师兄确认消息后,倍感震惊和遗憾。
虽然直接打交道,并没有几次,但同在一个NLP小圈子,间接的人际关系也不少,也去过创业公司的办公地址参观。
人还很年轻,很有理想。一个在深度学习早期改变NLP解决范式的时候,就积极拥抱深度学习的先驱。给实验室的师兄们提供了早期的深度学习实习机会,这也后来影响了我们这些师弟师妹们的择业路径。一个在创业圈,坚持了好多年的前辈。
悲伤,遗憾。
快跨年了,大家都在规划休假,总结和展望,却有人永远停留在了2025年。你所不在乎的今天,是他人奢求不到的明天。真的是人生无常。去者当怀思,生者当勉励,且行且珍惜。
我是豆包的重度使用者
我使用豆包的设备,主要是PC端。因为在办公日,主要的时间是在面向一台macbook进行办公。豆包主要满足我需求的是:
- 知识问答需求方面,基本替换掉了搜索引擎。搜索引擎现在主要被用来找具体的资源页面(URL),比如,某个人的google scholar页面,某篇具体的论文等。对于寻找答案类的搜索query,豆包基本都能给到非常准确的答案。
- 生成一些文案。比如,一些评语,邮件等。我最近的一封关于苹果开发者账号问题,发给Tim Cook的邮件,就是豆包帮我写的。
- 翻译文本。
- 文章/论文解读。
- 生成代码。基本上是单个的功能文件。对于项目型的正规开发,我更多依赖VS Code上的Github Copilot 插件。
- 一些文本的格式化。比如,一个excel表内容,转成markdown或是latex格式。
我不太用的一些功能:
- 文生图。我个人的需求量小,且用过几次,效果一般。
- 打电话。我儿子喜欢给豆包打电话。我用过几次做英语练习,感觉用于增加对话轮次的引导类反问太多,比较压迫,不舒服。
对于豆包要在2026年春晚上亮相,个人感觉是个比较重要的时间节点。春晚上的推广,对于击穿“社会层级”、把一个稍显高端的AI产品,传递到所谓的“下沉市场”,是一个极好的机会。豆包自己做了很好的能力准备,在这次推广后,会彻底成为另一个新的国民级APP。会有大量新增用户,和不错的留存。
关于一些AI硬产品
【Rokid Glasses】
Rokid Glasses在一段时间内的自媒体平台上,热度较高。说是还卖断了货。创始人比较有意思,长相和年龄比较有GAP,创业非常有热情,还到微信来做talk。所以,买了Rokid,还特意定制了内贴的镜片,结论是体验并不太好。原因如下:
- 【佩戴不舒适】。智能眼镜首先应该是个眼镜,其次才是智能。这意味着,佩戴起来得舒服。Rokid眼镜的宽度对我这种大脸人士来说,如同受刑。镜体偏重,镜腿表面是光面的,容易下滑,镜框和镜腿易脏(指纹油渍收集器)。过大的黑边框面积,影响视野。这可能和我长期佩戴较为轻盈的无边框眼镜有关。一层屏幕+一层近视镜的原因,感觉影响了透光度。总之,由于佩戴的不舒适感,使它不可能成为我的日常眼镜。
- 【无刚需的功能】实时收看微信消息?这会不断和分散个人注意力,佩戴久了,可能会导致一些大脑问题。提词器?一个普通人,一个月又能做几次公开讲话?还是需要备稿和带稿的那种。翻译?最近没出国。一般的翻译需求,在PC端就搞定了。导航?步行或是骑行导航,基本上看一眼就知道路线了,不用实时导航。车载导航就用车上自带的或是手机就好了,画面效果好很多。蓝牙耳机?对于我这种经常听音乐,看短视频的,应该需求还比较强。但佩戴不舒适,又担心漏音,所以不会经常使用。
【Looki L1】
没买,判断下来没必要买。看上去是个具有AI能力的硬件设备,实际上AI能力在云端的算法后台。硬件只是个带存储的摄像头,类似于行车记录仪。个人每天的全量生活场景数据,上传到云端做分析的人,也是心大。无wifi的情况下,上传的流量应该消耗也比较大。借助于现在的VLM进行分析,要几个小时,时间代价较大。这种AI硬件是没有壁垒的,公司能否提供长期的维护能力和有无健全的隐私保护机制,是值得质疑的。
【其他硬件】
短视频平台上刷到过一个用于学英语的AI硬件,外观像个放大镜。拍一个物品,出现其英语单词和解释等。这种功能,有必要再来卖个硬件么?手机上下载个app,开一下摄像头不就ok了?眼看着很多打着AI旗号做创新硬件人,是在把手机中已经集成的功能,又拆出来,讲个垂直功能的故事。确实会有一些目标用户,比如,想让小孩在手机上用一下学英语的能力,又担心被用来打游戏或是刷短视频的家长们,可能买单。但是,我们不会再回到,出门一趟,兜里要装五六个设备的时代了。尤其做面向成年人AI硬件产品的同学,你的设备如果是特别垂直的功能,又和手机能力存在重叠。用户大概率买回来用一段时间,又会回归到手机。